Netflix Zuul Push
Zuul Push Architecture
Zuul Push is the push engine at Netflix
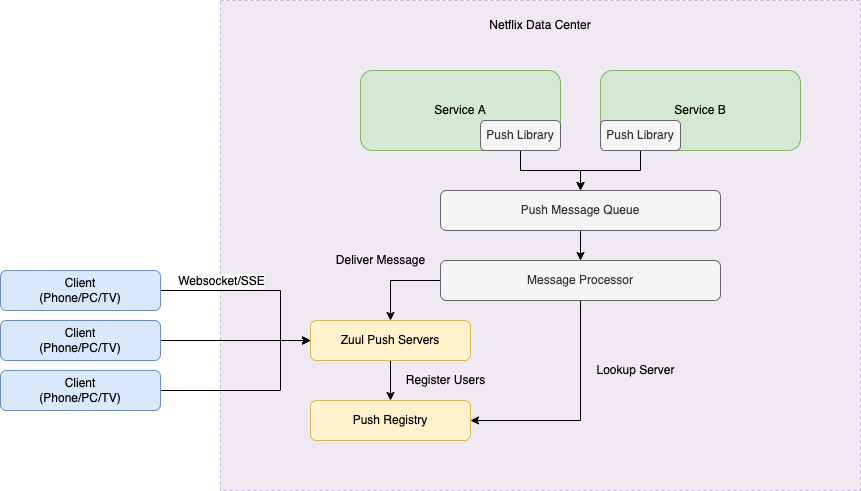
Workflow
- Client establishes an persistent websocket/SSE connection to the Zuul Push Service. The Client will keep the connection alive until the session is terminated.
- Zuul Push Service register the user and connection information to the Push Registry database.
- Service that need to send a push message (source of push message) use the Push Library (SDK) to send the message to the Push Message Queue.
- Message Processor
- pulls/retrieves an message from the Push Message Queue
- lookups the Push Registry to check which Zuul Push Service host is connected to the client
- delivers the message to the Zuul Push Service host
- Zuul Push Service host send the message to the Client
Background
Netflix use a recommendation engine to generate suggested videos for each user. i.e. the home page of the Netflix website for each user is different.
Push vs Pull
- Pull
- If too frequent - Overload the system
- If too infrequent - Data not fresh enough
- Push
- Most suited for Netflix
Push
Define Push:
- Persist
- Until
- Something
- Happens
The server push the data to the client instead of the client requests the data from the server.
Zuul push servers
Handling millions of persistent connections
Using Non-blocking async-io
C10K challengingL
- Supporting 10K concurrent connection on a single server
Traditional method:
- 1 Connection per Socket
- 1 Socket per thread
Socket --> Read --> Write --> Thread 1 Socket --> Write --> Read --> Thread 2
Async I/O
Socket --> write callback --> single thread --> read callback --> Socket
Netflix use Netty for the Async I/O
Push Registry
Push registry feature checklist (the database used as the push registry should have the following feature):
- Low read latency
- Record expiry (e.g. TTL)
- Sharding
- Replication
TTL -> If the client failed to terminated the connection proactively; the system need to use TTL to remove the registered entry from the Push registry.
Good choice for Push Registry
- Redis
- Cassandra
- AWS DynamoDB
Netflix use Dynomite
Dynomite = + Redis + Auto-sharding + Read/Write quorum + Cross-region replication
Message Processing
Message queuing + route delivery
Netflix use Kafka
Message sender use "FIRE and FORGET" approach:
- Drop the push message into the queue
- Carry on with other tasks
Cross-Region Replication
- Netflix use 3 AWS region
- Use AWS Kafka queue replication
Queue:
- Hard to use single queue
- Different queues for different priorities
Message processor
- multiple message process in parallel
- auto scale based on the number of message in the queue
Operating Zuul Push
Different from the Stateless services
Stateful:
- Persistent connections - long lived statble connection
- Great for client efficiency
- Terrible for quick deploy/rollback
Deploy/Rollback
- Client are not automatically migrate to the newly deployed servers
- Thundering herd: If keep the connection at once, the client would try to connect to the new servers at once (overwhelm the servers)
Solution:
- tear down connection periodically (from the server side)
- randomize each connection's lifetime (jitter)
- result: randomizing connection lifetime on reconnect peak
- Extra: server ask client to close its connection (the party terminate the TCP connection might have a FD on linux remain open for up to 2 mins)
Optimization
How to optimize push server? (most connection are idle)?
first approach: big ec2
- big EC2, as many connection on the single server as possible
- Issue: if a server is down: Thundering herd happends
second approach: goldilocks strategy (just right)
- m4.large (2v CPU)
- 84,000 concurrent connection per ec2
Optimize for cost, NOT for instance count
How to auto-scale ?
RPS (request per second) ? NO
- No RPS for push servers
CPU ? NO
- Instances is not limited by CPU
Open Connection ? YES
- Only factor that is important to a push server
AWS Elastic Load Balancer cannot proxy WebSocket
ELB does not understand websocket Upgrade request (A special HTTP request)
Solution: Run ELB as a TCP load balancer (NLB) (Layer 4)
AWS ALB not support WebSocket
Use case for Push System
- On-demand diagnostics
- Send special diagnostics to devises
- Remote recovery
- User messaging
References
- Susheel Aroskar- Scaling Push Messaging for Millions of Devices @Netflix